Introduction
In the intricate ecosystem of data centers, regulating the operating temperatures is an ongoing struggle. Servers and other IT apparatus emit substantial heat, precipitating a decline in efficiency. This is surging energy expenses, and the potential for equipment malfunction. To mitigate these issues, hot aisle containment (HAC) systems emerge as a pivotal strategy. They ingeniously segregate hot from cold air currents, significantly contributing to cooling mechanisms within data centers. This approach ensures that the machinery functions within permissible temperature thresholds, thus bolstering performance and longevity. This exposition delves into the nuances of hot aisle containment, shedding light on its myriad advantages. The essential components that constitute such systems, and the methodologies for their deployment. Furthermore, it endeavors to clarify prevalent inquiries pertaining to this efficacious cooling methodology. This is providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of its importance and utility.
What is Hot Aisle Containment?
Hot aisle containment (HAC) represents a sophisticated strategy in data center cooling, aiming to refine the effectiveness of cooling apparatus. By orchestrating a physical demarcation between the hot air discharged, IT hardware and the cooler air that feeds into the equipment. This technique entails the encapsulation of the hot aisle—the area where the rear of servers expel heat—employing doors, roofs, and in certain instances, walls. The primary goal is to encapsulate and reroute the heated exhaust air directly back to the cooling mechanisms, such as Computer Room Air Conditioning (CRAC) units or Computer Room Air Handlers (CRAH). Thereby preventing its amalgamation with the incoming cool air. Such a methodological approach is instrumental in bolstering airflow and thermal regulation within the data center. This is culminating in notable enhancements in cooling productivity and energy efficiency.
Implementing HAC not only mitigates the risk of hot and cold air streams intermingling but also ensures a more targeted cooling process. Which can significantly reduce the operational costs associated with energy consumption. Moreover, this cooling strategy plays a extending the lifespan of critical IT equipment by maintaining optimal operational temperatures. The integration of HAC systems demonstrates a commitment to sustainability. As it allows for a substantial reduction in carbon footprint by optimizing energy use.
This advanced cooling solution underscores the importance of strategic airflow management within data centers Highlighting how technological innovation can lead to more sustainable and efficient operational practices. By adopting hot aisle containment, data centers can achieve a balance between technological performance and environmental responsibility, setting a new standard in the industry for energy management and equipment reliability.
Benefits of Hot Aisle Containment
Sustainability
The deployment of hot aisle containment (HAC) systems within data centers heralds a multitude of benefits. This is marking a significant leap towards operational excellence and sustainability. At its core, HAC enhances cooling efficiency by establishing a clear demarcation between the hot air emitted by IT equipment and the cooler air intended for cooling. This strategic segregation ensures that cooling mechanisms can function with heightened efficacy. Thereby fostering a more uniform temperature distribution throughout the facility. This not only elevates the environmental conditions for both machinery and personnel, promoting safety and comfort. But also underscores the system’s inherent efficiency.
Reduction in Expenses
One of the standout advantages of implementing HAC is the tangible reduction in cooling-related expenses. By fine-tuning the cooling process, data centers witness a marked decrease in energy consumption. This, in turn, translates to lowered operational costs, offering significant financial relief over time. Furthermore, the energy efficiency achieved through HAC directly contributes to environmental stewardship. By diminishing the need for excessive energy use, data centers can significantly lower their carbon footprint, aligning their operations with broader sustainability goals.
Moreover, HAC’s role in bolstering IT equipment performance cannot be overstated. The system ensures that devices operate within their ideal temperature ranges, effectively minimizing the risk of overheating. This precautionary measure not only mitigates the likelihood of hardware failures but also contributes to prolonging the lifespan of critical data center assets. The cumulative effect of these advantages is a more resilient, efficient, and sustainable data center environment. By adopting HAC, data centers not only optimize their cooling strategies but also set a precedent for operational excellence that balances technological innovation with environmental responsibility.
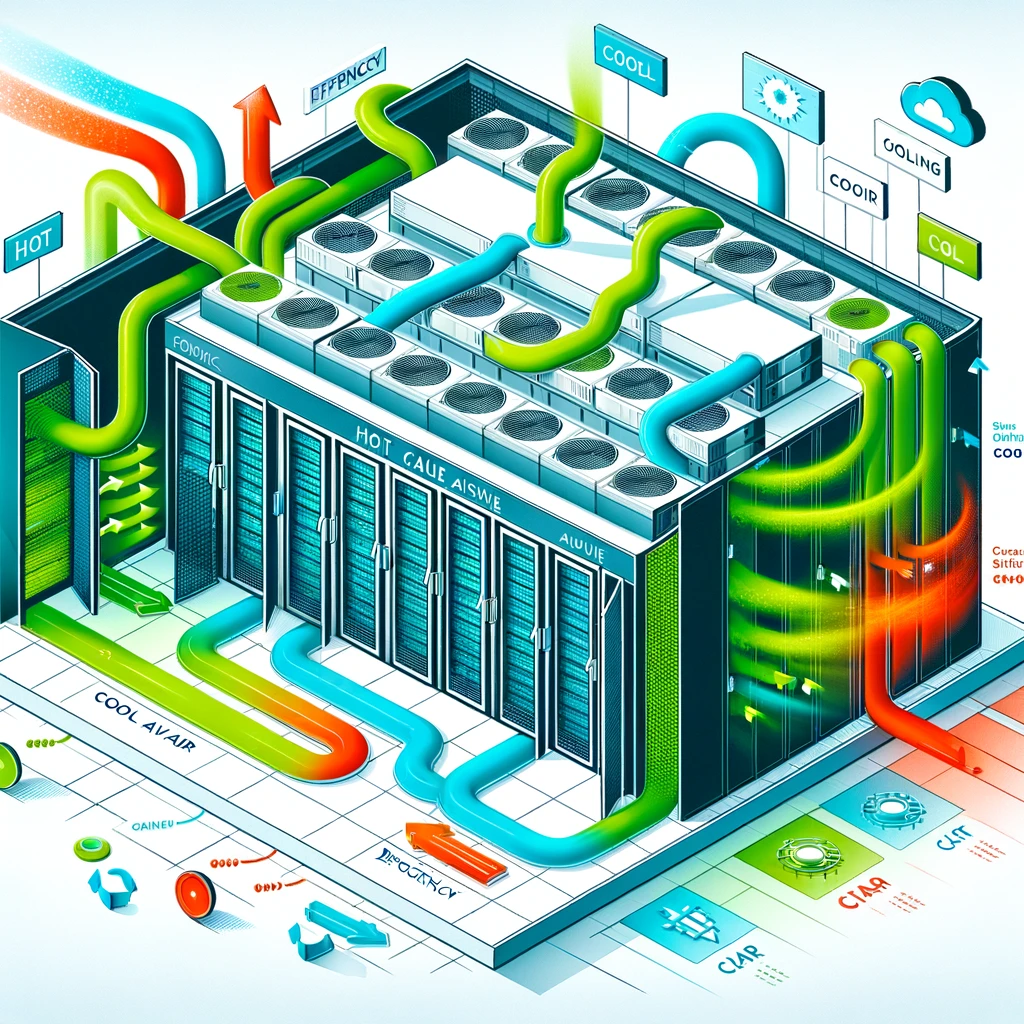
Key Components of a Hot Aisle Containment System
Optimizing the Cooling Process
Implementing a hot aisle containment (HAC) system in data centers involves integrating a series of essential components. Making them work together to segregate hot air from cooler air, thereby optimizing the cooling process. The foundation of HAC is established through the use of physical barriers such as doors, modular walls, and ceiling panels. These are strategically placed to enclose the hot aisle. This configuration effectively traps the hot air emitted by server racks, preventing it from mingling with the cooler ambient air prevalent in other parts of the data center. These barriers are meticulously designed to integrate seamlessly with the data center’s pre-existing cooling infrastructure. Including Computer Room Air Conditioning (CRAC) units and Computer Room Air Handlers (CRAH), ensuring the efficient extraction of hot air from the contained space.
Airflow Management
To augment the efficacy of HAC, airflow management accessories play a crucial role. Blanking panels and brush strips are to employ to fill voids in the rack spaces and around cabling. Thereby mitigating air leakage and ensuring that the cooling air is directing where it precisely where it is most needed. Additionally, raised floor systems offer a strategic advantage by facilitating the direct delivery of cooled air to the cold aisles. This design choice enables a more targeted and consistent cooling methodology. This is ensuring that cool air reaches the front of the servers without dilution by the hot exhaust.
Together, these components form a cohesive system enhances cooling efficiency and energy utilization. Also contributes to the overall thermal management of the data center. By meticulously sealing off the hot aisle and employing tools to manage airflow and direct cooling, data centers can achieve a more controlled and effective cooling environment. Leading to improved operational efficiency and equipment performance.
Implementing Hot Aisle Containment in Your Data Center
Implementing hot aisle containment requires careful planning and design. This is to ensure compatibility with the data center’s existing layout and cooling infrastructure. Key considerations include the size and configuration of the data center, the type of IT equipment, and the existing cooling solutions. Data center infrastructure management (DCIM) tools can provide valuable insights into thermal patterns and airflow. This is aiding in the design of an effective containment system.
The installation process involves setting up the physical barriers, configuring the cooling units, and ensuring proper airflow management. Best practices include conducting airflow analysis to identify potential leakage points and using adjustable containment solutions to accommodate future changes in equipment layout or cooling needs.
Retrofitting data centers with hot aisle containment can pose challenges, such as space constraints or compatibility with existing infrastructure. However, with careful planning and the use of modular containment solutions, these challenges can be overcome, allowing older data centers to benefit from improving cooling efficiency and energy savings.

FAQs on Hot Aisle Containment
- What is the difference between hot aisle and cold aisle containment? A: Hot aisle containment focuses on enclosing the hot air exhaust aisles, directing the hot air back to cooling units. Cold aisle containment encloses the cold air intake aisles, ensuring that cold air is directed toward server intakes without mixing with hot air.
- How does hot aisle containment affect cooling costs? A: Hot aisle containment improves cooling efficiency by preventing hot and cold air mixing, allowing cooling systems to operate more effectively and at lower costs.
- Can hot aisle containment be retrofitted in an existing data center? A: Yes, hot aisle containment can be retrofitted in existing data centers. Modular and adjustable containment solutions make it possible to implement HAC systems without significant disruptions to data center operations.
Conclusion
Hot aisle containment is a proven strategy for enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of data center cooling systems. By effectively managing airflow and optimizing thermal management, hot aisle containment can lead to significant energy savings. As well as reduced cooling costs, and improved performance and lifespan of IT equipment. Whether planning a new data center or retrofitting an existing facility, considering hot aisle containment is a step toward achieving operational excellence and sustainability in the ever-evolving landscape of data center management.