Introduction
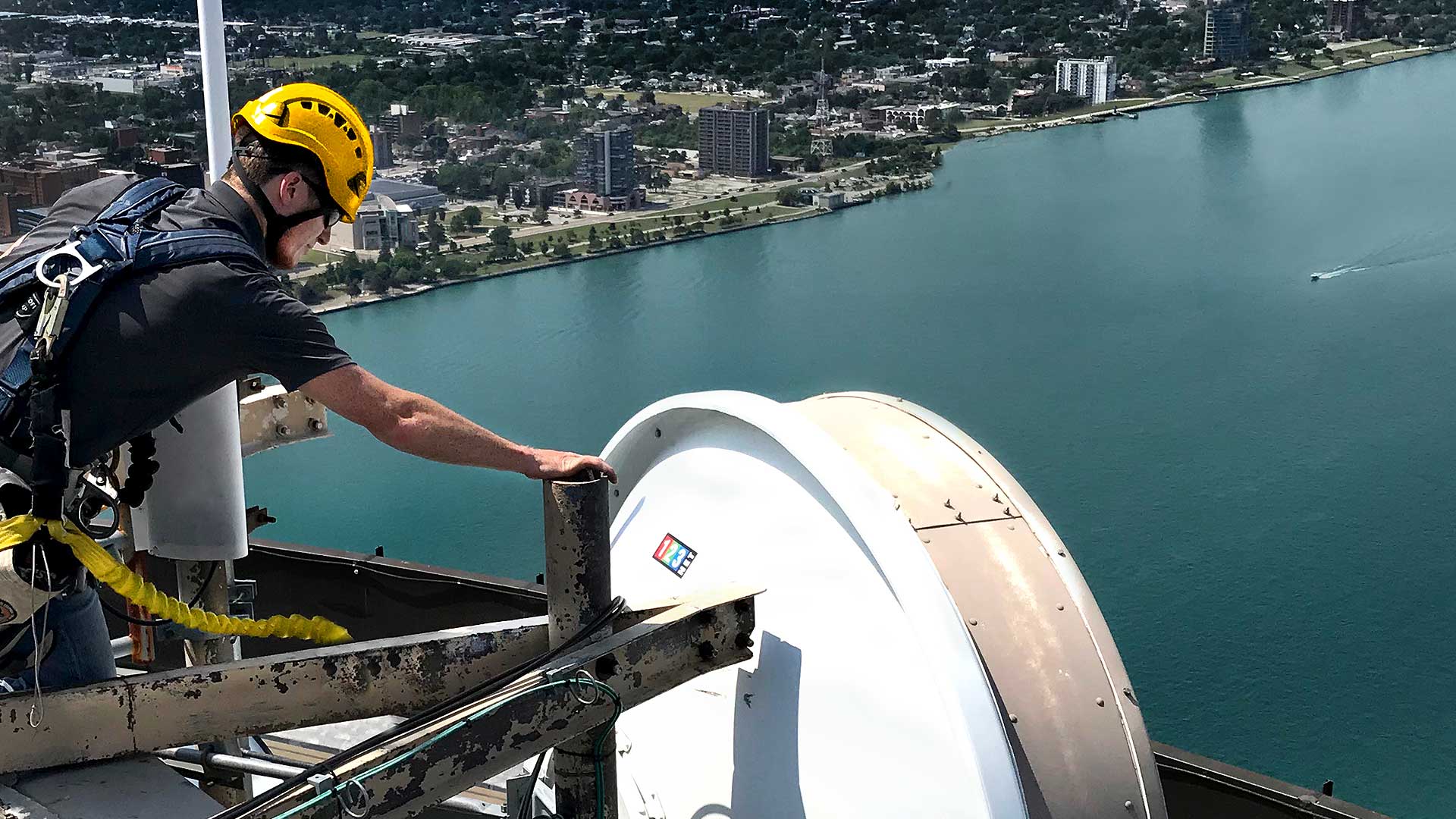
Fiber-To-The-Home (FTTH) technology represents a revolution in broadband connectivity, offering unprecedented internet speeds and reliability. This innovation utilizes optical fibers, a stark contrast to the traditional copper wires, for data transmission. This transition to optical fibers enables significantly faster and more stable internet connections, which are crucial for the modern digital lifestyle. FTTH not only elevates the user experience but also meets the growing demands for high-bandwidth applications such as streaming services, online gaming, and remote work. In this digital age, where internet connectivity is as essential as utilities, FTTH emerges as a key technology, providing the backbone for an increasingly connected world. The adoption of FTTH is rapidly transforming internet infrastructure, offering a future-proof solution that supports the ever-expanding data needs of both individuals and businesses. This technology is setting new benchmarks in internet speed and quality, making it a cornerstone of today’s digital era.

The Evolution to FTTH
The evolution of FTTH (Fiber-To-The-Home) technology since the 1980s is a remarkable journey of innovation and growth. In the early stages, the use of optical fiber for telecommunications was a groundbreaking concept. Initially, fiber optics were mainly used for long-distance telephone signaling, offering a significant improvement over traditional copper wire methods due to their higher bandwidth and lower signal loss.
By the late 1990s and early 2000s, the potential of fiber optics extended beyond these long-distance applications, leading to the conceptualization of FTTH. This transition was driven by the increasing demand for higher internet speeds and the limitations of existing copper and coaxial cable networks. Pioneers in the field began experimenting with bringing fiber optic cables directly to homes and businesses, offering unprecedented internet speeds.
The 2010s saw a rapid acceleration in FTTH deployment, as technological advancements made it more cost-effective and the demand for high-speed internet surged. With each passing year, FTTH became more accessible, transforming from a luxury to a necessity in many regions. Today, FTTH is a critical infrastructure for supporting the data-intensive needs of modern society, from streaming high-definition content to enabling smart homes and cities.
The Growth and Expansion of FTTH
In recent years, the U.S. has experienced a significant surge in Fiber-To-The-Home deployment. Statistics demonstrate a consistent increase in FTTH adoption, significantly outpacing traditional copper broadband in terms of speed and efficiency. This remarkable growth is not confined to urban areas; rural regions are also increasingly reaping the benefits of FTTH. This expansion plays a crucial role in diminishing the digital divide, ensuring more equitable internet access across various demographics.
FTTH’s superiority over slower and less dependable copper networks is evident. It offers a groundbreaking solution, redefining internet connectivity standards. FTTH’s optical fiber technology ensures ultra-high-speed internet, a necessity for today’s data-heavy activities like streaming high-definition content, engaging in seamless online gaming, and supporting robust telecommuting environments.
This technological shift is not just about enhanced internet speeds; it represents a fundamental change in how communities access and use digital resources. FTTH’s widespread implementation is fostering new opportunities in education, healthcare, and business, contributing to local economies and enhancing the quality of life.
In essence, FTTH is more than just an upgrade in internet technology – it’s a catalyst for broader social and economic transformation, propelling the U.S. towards a more connected and digitally inclusive future.
Understanding the Technology
FTTH (Fiber-To-The-Home) is a type of fiber optic communication delivery in which the fiber extends from the main telecommunications switch directly to a residence or business, providing unmatched high-speed internet connectivity. This direct approach contrasts significantly with other FTTx technologies like FTTB (Fiber-To-The-Building), FTTN (Fiber-To-The-Node), and FTTC (Fiber-To-The-Curb).
FTTB, similar to FTTH, involves fiber optic cables running to a building or complex. However, in FTTB, the connection typically ends at a common point in the building, such as a basement or a central communications room, and other types of cabling then carry the signal to individual units or offices.
FTTN, on the other hand, extends fiber to a cabinet or node that could be several kilometers away from the user’s premises. The connection from this node to individual homes or businesses is often made using copper wiring. This results in lower speeds compared to FTTH due to the limitations of copper cabling.
Similarly, FTTC brings the fiber closer to the user than FTTN — usually to the curb or sidewalk near the residence — but still relies on copper wires for the final few meters or kilometers. This approach offers better speeds than FTTN but doesn’t match the direct fiber connection of FTTH.
In essence, while all these FTTx technologies utilize fiber optic cables, the key difference lies in the last mile of connectivity. FTTH provides the most direct and fastest connection, making it the superior choice for high-speed internet access.

Benefits of FTTH over Coax and DSL
The advantages of FTTH (Fiber-To-The-Home) over coaxial and DSL connections are significant and multi-faceted. Firstly, FTTH offers superior speed. Fiber optic technology enables data transmission at much higher rates than coaxial and DSL, making FTTH networks capable of handling gigabit speeds, essential for modern internet demands.
Secondly, FTTH provides a more reliable connection. Fiber optics are less susceptible to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation over long distances, unlike copper-based DSL and coaxial cables. This results in a more stable and consistent internet experience, which is particularly beneficial for high-bandwidth activities like video conferencing and online gaming.
Furthermore, FTTH boasts a longer lifespan and lower maintenance requirements. The durability of fiber optic cables means they are less prone to wear and tear compared to coaxial and DSL cables. This longevity makes FTTH a more cost-effective solution in the long term.
Lastly, FTTH supports future technological advancements. As internet technologies evolve and demand for higher bandwidths grows, the superior capacity of fiber optic cables ensures that FTTH networks can accommodate these future needs without the need for extensive overhauls. This forward compatibility is a key advantage in an era of rapid technological change.
FTTH Deployment Strategies and Challenges
The deployment of FTTH (Fiber-To-The-Home) networks is a complex endeavor that requires meticulous planning and precise execution. Service providers must navigate a maze of logistical challenges, with supply chain disruptions often at the forefront. These disruptions can delay the delivery of crucial materials, affecting the overall timeline and cost of network expansion. Effective deployment strategies are, therefore, critical to overcome these hurdles and ensure timely, cost-efficient rollouts.
Another significant challenge in FTTH deployment is the diverse and sometimes difficult terrain. Providers must plan routes through urban landscapes, rural areas, and sometimes challenging topographies, each presenting unique obstacles. The complexity is further increased by the greatly varying distances that need to be covered for network expansion. These factors require tailored solutions and innovative engineering approaches to ensure efficient fiber optic cable laying.
Community engagement is another crucial aspect of successful FTTH deployment. Gaining the trust and support of local communities is essential. Providers often need to work closely with local authorities, residents, and businesses to minimize disruptions and address concerns. This collaboration is key to smoothly integrating the new infrastructure within existing environments.
Overall, deploying FTTH networks is a balancing act that involves addressing technical, logistical, and social factors. Success in this endeavor not only advances technology but also bridges digital divides, making it a vital undertaking in today’s increasingly connected world.
FTTH and Its Role in Modern Internet Usage
This technology significantly impacts various aspects of modern internet usage, reshaping how we engage in activities such as eCommerce, online banking, remote work, and the utilization of Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
In the realm of eCommerce, FTTH’s high-speed connectivity facilitates a seamless shopping experience, supporting high-definition product visuals and live customer support, which are critical for customer satisfaction and business growth. Online banking, a sector that demands both speed and security, also benefits immensely from FTTH. The fast and stable connections provided by FTTH ensure smooth, uninterrupted online transactions and enhance the overall user experience in handling sensitive financial operations.
The surge in remote work, accelerated by recent global events, underlines the importance of reliable internet connections. FTTH’s high-speed and stable connectivity support video conferencing, large file transfers, and constant online presence, which are essential for effective remote working environments.
Lastly, the IoT ecosystem, which is rapidly expanding into homes and businesses, relies heavily on a robust internet backbone. FTTH provides the necessary bandwidth and speed to support multiple IoT devices, from smart home appliances to sophisticated security systems, ensuring seamless communication and data transfer within the IoT network.
Overall, FTTH stands as a cornerstone in today’s digital landscape, enabling a plethora of internet-dependent activities with enhanced efficiency and reliability, thereby playing a pivotal role in the evolution of modern internet usage.
123NET as a FTTH Provider
123NET has emerged as a significant player in the Fiber-To-The-Home (FTTH) technology space, offering high-speed, home fiber internet services. This service is a perfect fit for the modern digital lifestyle, catering to the needs of streaming, gaming, and smooth video chats, ideal for families and individuals alike. Here’s how 123NET aligns with the FTTH technology and its benefits:
- High-Speed Internet Plans: 123NET provides various internet plans, including 250 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 2Gbps, and 6 Gbps options. These plans are designed to cater to different user needs, from downloading large files and streaming services to professional gaming. The 100% fiber network ensures that the connection is always stable, with matching download and upload speeds.
- No Data Caps and Equal Download & Upload Speeds: One of the standout features of 123NET’s FTTH service is the absence of data caps, offering unlimited bandwidth. This feature is crucial for users who engage in data-intensive activities like streaming in high definition, rapid file sharing, lag-free gaming, and uninterrupted video conferencing.
- Flexible and User-Friendly Service: 123NET offers a no-contract service, allowing users to change or switch their internet service anytime without worrying about long-term commitments. This flexibility is particularly appealing in the fast-evolving internet service market.
- Building Network for Enhanced Connectivity: 123NET is focused on building a network to make Michigan communities and businesses among the best connected on the planet. This commitment to infrastructure development is crucial for the widespread adoption and effectiveness of FTTH technology.
- Advanced WiFi Technology: The service includes advanced WiFi technology that minimizes dead zones and supports high-density WiFi usage. This means a stable and smooth WiFi connection throughout the home, essential for a seamless online experience.
Evolvement & Conclusion
The journey of FTTH (Fiber-To-The-Home) technology, from its inception to its current status, underscores a significant transformation in global internet infrastructure. FTTH has evolved from a niche, high-end option to a widely recognized and essential service. This attributes to the rapid growth of digital activities in both personal and professional spheres.
As we look towards the future, FTTH stands poised for even greater expansion. There is an increasing demand for high-speed internet, driven by data-intensive applications like 4K streaming, cloud computing, and IoT devices. This ensures FTTH’s relevance and necessity. The ongoing innovations in fiber optic technology promise to further enhance the capabilities of FTTH networks. This will lead to potentially offering even faster speeds and more reliable connections.
The future outlook for FTTH also includes broader accessibility. Efforts to bridge the digital divide, especially in underserved rural areas, are likely to focus on expanding FTTH infrastructure. This is recognizing its role in fostering economic growth, educational opportunities, and overall community development.
In conclusion, FTTH technology is not just a part of our present internet landscape but a cornerstone of future digital advancements. Its continuous evolution will likely shape the way we interact with technology, emphasizing speed, efficiency, and connectivity.
FAQ Section
- How does FTTH compare to other broadband technologies?
- FTTH is often considered superior to other broadband technologies such as DSL and cable internet. It provides the fastest speeds and the most reliable connection, especially when compared to FTTN (Fiber-To-The-Node) and FTTC (Fiber-To-The-Curb), where the fiber optic cable is terminated at a node or street cabinet, and then traditional copper wire is used for the final connection to homes or businesses.
- What challenges come with FTTH deployment?
- The deployment of FTTH involves significant initial installation costs due to the laying of fiber optic cables. Also, its availability can vary, with rural or remote areas having limited access to this technology. However, these challenges are often outweighed by the long-term benefits and reduced maintenance costs.
- Is FTTH environmentally friendly?
- FTTH is considered more environmentally friendly than other broadband technologies. Fiber optic cables are made of glass or plastic, which are recyclable materials. They are also thinner and lighter, requiring less energy for transportation and installation. Furthermore, FTTH’s durability reduces the need for frequent upgrades or replacements, contributing to lower waste and CO2 emissions.
- How does the installation process of FTTH work?
- Installing FTTH is typically a streamlined process involving minimal disruption. Fiber optic cables are usually installed underground or along existing utility poles, causing limited inconvenience to users.